Google ($GOOGL) Wins Java Copyright Case Against Oracle ($ORCL)
A federal jury here ruled that Google’s use of Oracle Corp.’s Java software didn’t violate copyright law, the latest twist in a six-year legal battle between the two Silicon Valley titans.
Oracle sued Google, a unit of Alphabet Inc [stckqut]GOOGL[/stckqut] [stckqut]GOOG[/stckqut]., in 2010 for using parts of Java without permission in its Android smartphone software. A federal appeals court ruled in 2014 that Oracle [stckqut]ORCL[/stckqut] could copyright the Java parts, but Google argued in a new trial this month that its use of Java was limited and covered by rules permitting “fair use” of copyright material.
A 10-person jury on Thursday agreed.
Google acknowledged using 11,000 lines of Java software code. But it said that amounted to less than 0.1% of the 15 million lines of code in its Android mobile-operating system, which runs most of the world’s smartphones.


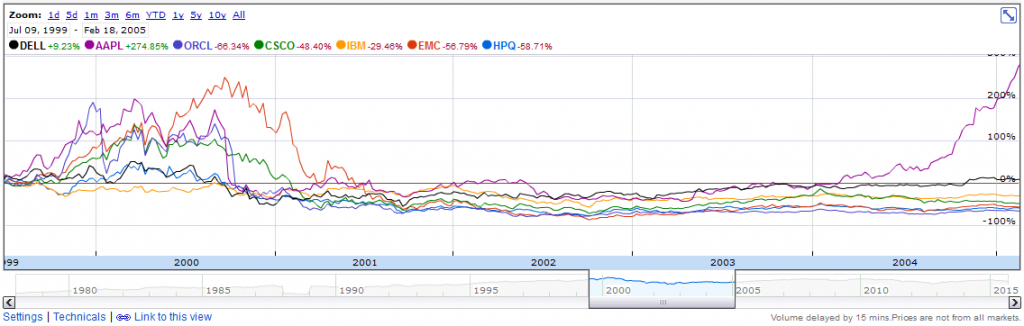
 Carly Fiorina is currently a candidate for President of the United States of America. She is campaigning for the nomination of the Republican Party to run in the general election of 2016. According to her, one of her strengths is her business background. Most notable she speaks of her background as the first CEO of a DOW30 company: Hewlett-Packard [stckqut]HPQ[/stckqut].
Carly Fiorina is currently a candidate for President of the United States of America. She is campaigning for the nomination of the Republican Party to run in the general election of 2016. According to her, one of her strengths is her business background. Most notable she speaks of her background as the first CEO of a DOW30 company: Hewlett-Packard [stckqut]HPQ[/stckqut]. Ironically, her record at HP is one of the criticisms of Ms. Fiorina. Donald Trump is famous for criticizing her as a failed CEO, and he often cites
Ironically, her record at HP is one of the criticisms of Ms. Fiorina. Donald Trump is famous for criticizing her as a failed CEO, and he often cites